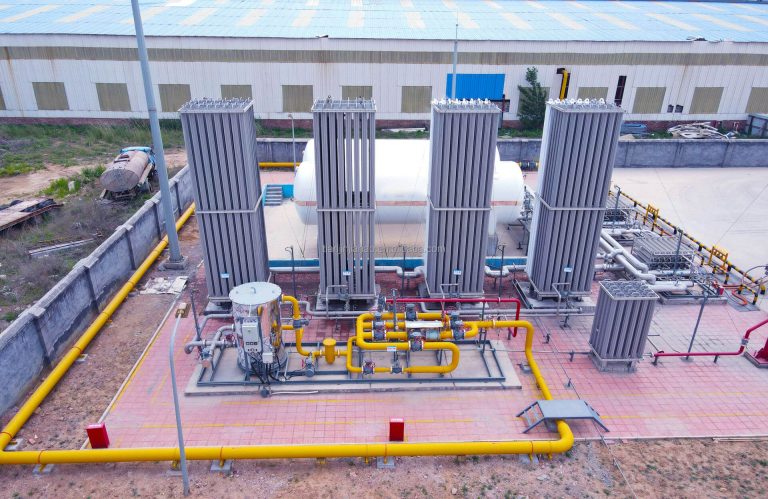
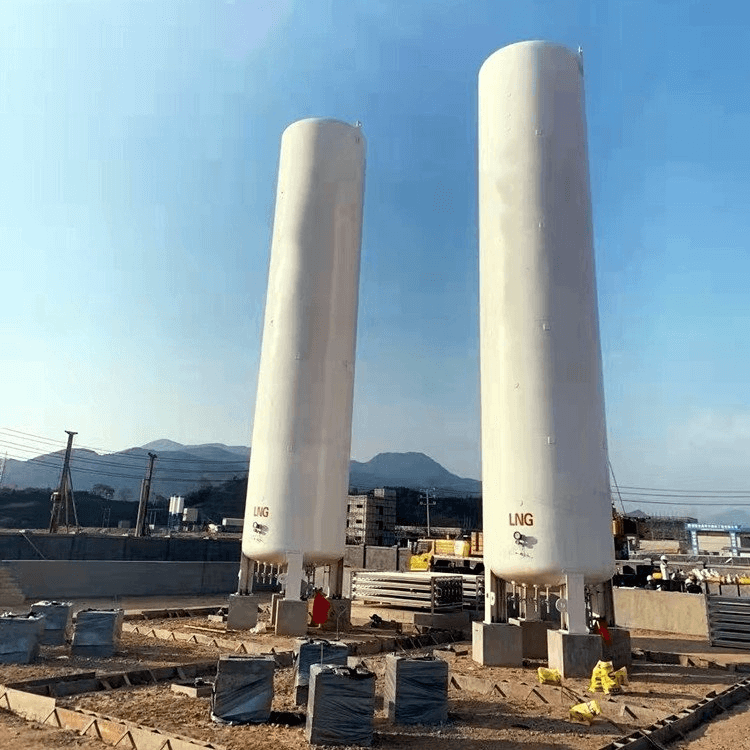
Liquefied natural gas (LNG), as an important component of clean energy, its storage technology is directly related to the safety and economy of energy supply. In the field of large LNG storage tanks, the following three mainstream storage methods are currently widely adopted, each with its unique technical features and applicable scenarios.
1.Large-scale cryogenic storage tanks for liquefied natural gas: Basic solution
Cryogenic storage tanks are the most traditional method for LNG storage. They feature a double-layer structure design, with the inner layer made of cryogenic materials and the outer layer being an insulation layer. This design maintains the liquid state of LNG at an extremely low temperature (-162°C), avoiding evaporation losses. The advantages of cryogenic storage tanks lie in their high technological maturity and low maintenance costs, making them suitable for small and medium-sized storage needs. However, its heat preservation performance is relatively limited, and the evaporation rate is relatively high during long-term storage. Therefore, it is more suitable for short-term or frequently turnover storage scenarios.
2.Mother and child tanks: A model of flexibility and modularization
The mother-child tank adopts a combination design of an outer tank with a flat-bottomed dome structure and multiple sub-tanks, with perlite sand filled in the interlayer to enhance the insulation performance. Sub-tanks are usually cylindrical in shape. They are prefabricated in the factory and inspected as qualified before being transported to the site for installation. This modular design not only simplifies the installation process but also enhances the flexibility of the storage system, allowing the number of sub-tanks to be adjusted according to demand. Another significant advantage of the mother-and-child tank is the short on-site construction period, which is suitable for space-constrained or temporary storage needs. However, its storage capacity is relatively limited and it is more suitable for medium-sized projects or distributed energy sites.
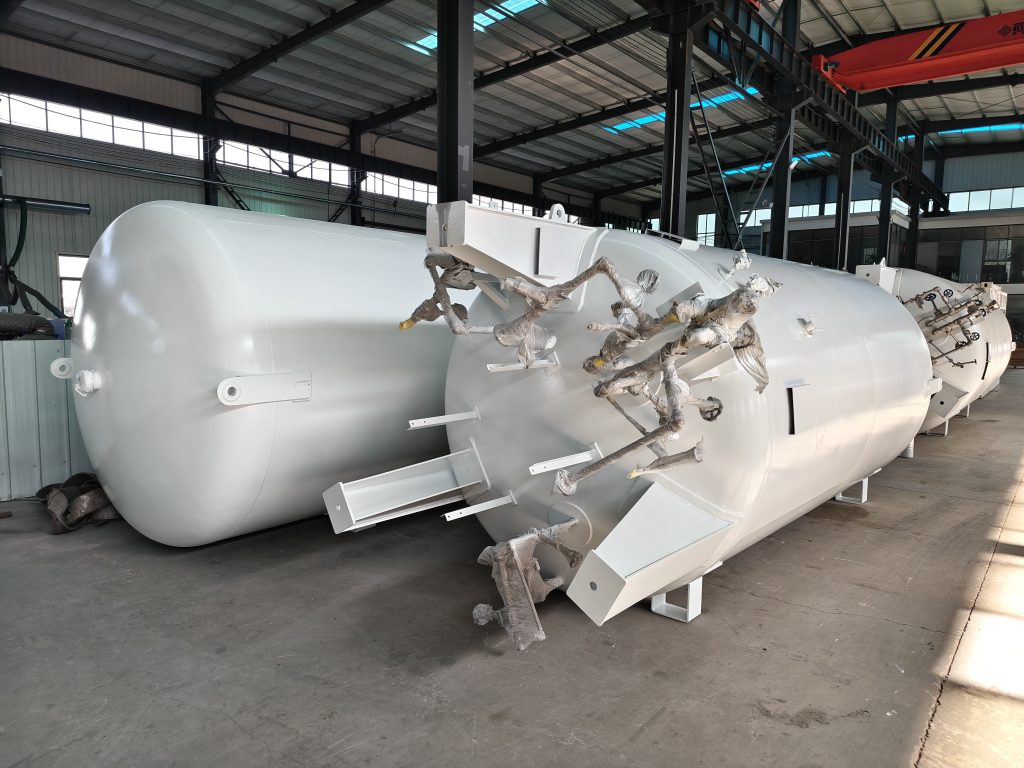

3.Spherical tanks: Representatives of large capacity and high performance
The spherical tank adopts a spherical design. Both the inner and outer tanks are spherical, or the outer tank is cylindrical and the inner tank is spherical. The interlayer is also filled with perlite. This structure enables the spherical tank to perform exceptionally well in terms of uniform force distribution and load-bearing capacity, while also having excellent cold insulation performance and significantly reducing the evaporation rate. The factory-prefabricated spherical disc design of the spherical tank further enhances the installation accuracy, but the construction difficulty and installation requirements are relatively high, and it requires a professional team to operate. Despite its high cost, spherical tanks have become the preferred choice for large-scale LNG receiving terminals and long-term storage projects due to their large capacity and high efficiency.
Technology comparison and future trends
The three methods each have their own focuses: cryogenic storage tanks are suitable for basic needs, mother-and-child tanks are known for their flexibility, while spherical tanks are dedicated to high performance and large capacity. With the growth of LNG demand, spherical tank technology, due to its high efficiency and environmental friendliness, is gradually becoming the mainstream in the industry. In the future, with the advancement of materials science and construction technology, these three methods will continue to be optimized to meet the diverse demands of the global energy transition.