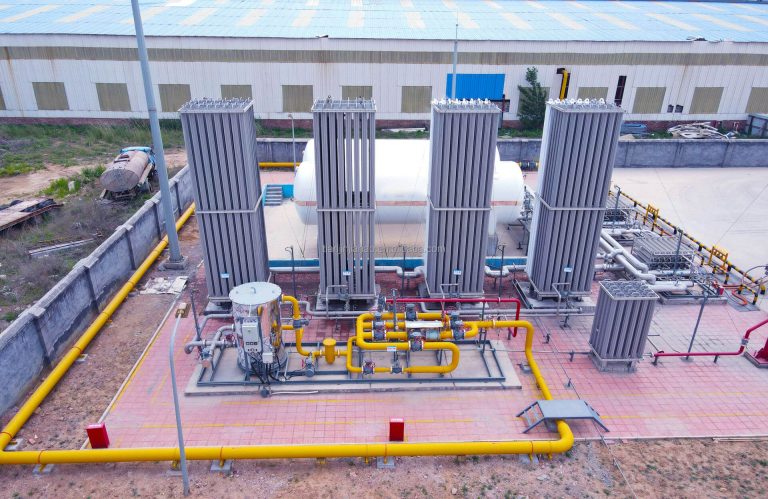
I. Development and Application Scenarios of cryogenic Storage Tanks Industry
With the continuous expansion of the application scenarios of low-temperature liquids such as LNG (liquefied natural gas), liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, liquid nitrogen, liquid helium, liquid argon and liquid CO₂, the demand for low-temperature liquid storage and transportation equipment in various industries has experienced an explosive growth. Since the reform and opening up, internationally renowned gas enterprises have set up joint ventures in China, not only introducing advanced air separation equipment and core technologies, but also bringing mature industry management experience, which directly led to a significant increase in China’s production of low-temperature liquids and the rapid rise of the low-temperature liquid storage tank industry, making it an indispensable emerging industry in energy, chemical, medical, aerospace and other fields.
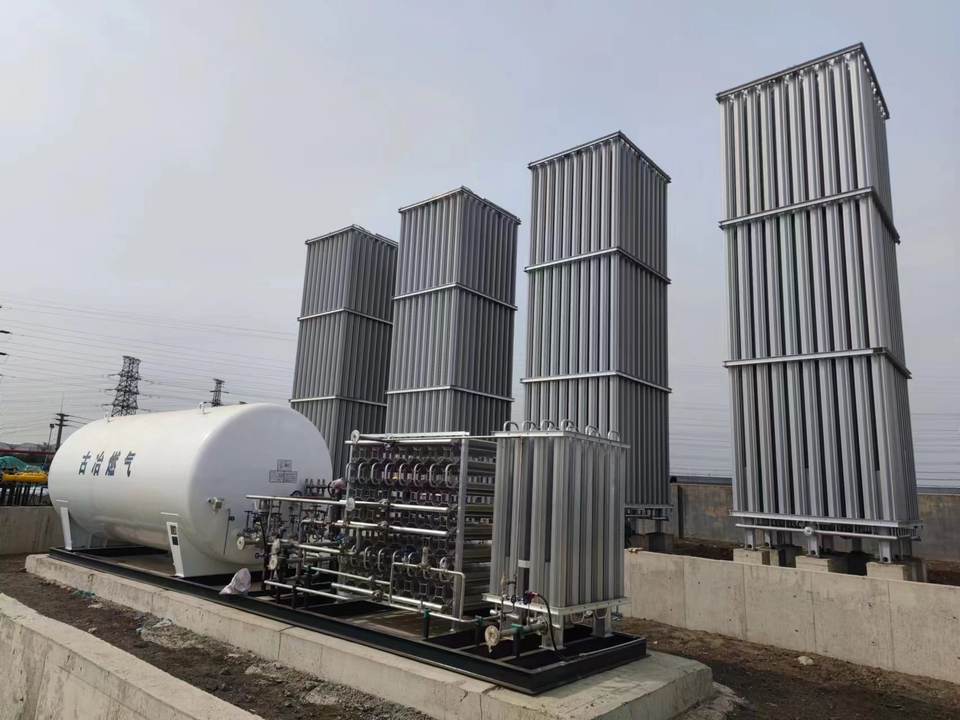

II. Core Structure and Technical Principles of cryogenic storage tanks
The core of the design for cryogenic storage tanks lies in “thermal insulation to prevent heat loss”. Its structure and process are highly specialized:
1.Shell material: The outer shell of the storage tank is made of high-quality container steel. The core advantage is that it does not come into direct contact with low-temperature media, effectively preventing the material from cracking due to low temperatures and ensuring the overall structural stability of the equipment.
2.Insulation layer process: Currently, the mainstream method employs the “pearlite sand filling + high vacuum extraction” technology. By leveraging the low thermal conductivity of the pearlite sand and the heat insulation effect of the vacuum environment, it aims to completely block the entry of external heat and reduce the gasification loss of the low-temperature liquid.
3.Key Technical Indicators – Evaporation Rate: The evaporation rate is the core parameter for evaluating the insulation performance of low-temperature storage tanks. For LNG storage tanks, the industry standard is typically ≤ 0.2% (daily average). This indicator is defined as: within 24 hours, the percentage of the volume of the low-temperature liquid in the inner liner that vaporizes due to heat leakage from the insulation layer, compared to the total volume of the storage tank. A lower evaporation rate indicates better insulation performance of the tank and higher efficiency in liquid storage and transportation.
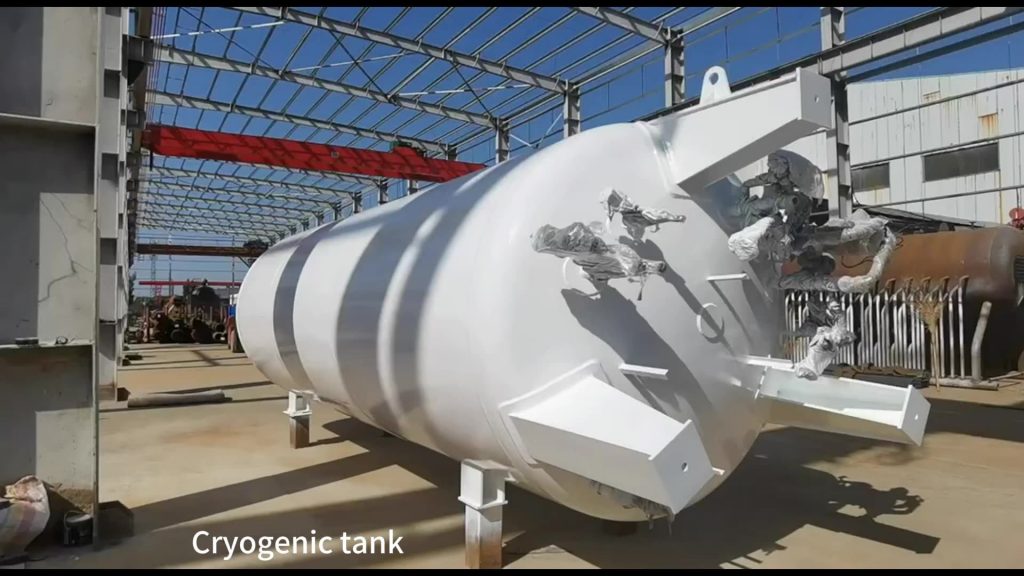

III. Correct Usage Methods of cryogenic storage tanks
1.Pre-job preparation: Operators must undergo professional training to be familiar with the model, rated volume, design pressure and low-temperature medium characteristics of the storage tanks (such as the flammability and explosiveness of LNG, the supporting combustion property of liquid oxygen, and the high-risk nature of liquid hydrogen, etc.), and must hold relevant certificates to work.
2.Inspection Process: Before use, each component such as the pressure gauge of the storage tank, the level gauge, the safety valve, and the emergency shut-off valve must be checked to ensure they are functioning properly. The vacuum degree of the insulation layer must also meet the standards. There should be no leakage at the pipe connections. All safety devices must be confirmed to be in an effective state.
3.Filling operation: Fill the tank strictly according to the rated filling capacity. It is prohibited to overfill (the filling volume should not exceed 95% of the total volume). To prevent the sudden increase in pressure inside the tank due to the expansion of low-temperature liquids when heated; during filling, control the flow rate to prevent the medium from splashing and causing low-temperature frostbite or other hazards.
4.Storage and Maintenance: The storage tanks should be placed in a dedicated area with good ventilation, far away from fire sources, heat sources and densely populated areas, and protected from direct sunlight. Regularly monitor the pressure and liquid level inside the tanks, keeping the pressure within the designed range. If the pressure abnormally rises, it is necessary to release the pressure through safety valves or vent valves in a reasonable manner.
5.Discharge / Output Operation: Before discharging, ensure that the receiving equipment meets the requirements of the medium. When connecting the pipelines, perform proper sealing treatment. Slowly open the valve and control the discharge speed to avoid excessive medium flow rate which may cause static electricity. During the operation, continuously monitor the pressure changes and stop the operation immediately if any abnormalities are detected.
IV. Safety Precautions for cryogenic storage tanks
1.Low-temperature protection: Contact with low-temperature liquids (such as LNG with a boiling point of -162℃ and liquid oxygen with a boiling point of -183℃) on the skin can cause instant frostbite. Operators must wear special cold-protective clothing, protective gloves, goggles and other protective equipment. It is strictly prohibited to touch the inner tank, pipelines or leaked media with bare hands.
2.Explosion-proof and Fire Prevention: For storage tanks of flammable and explosive media such as LNG and liquid hydrogen, the site must be equipped with combustible gas detectors and explosion-proof electrical equipment. It is prohibited to bring any ignition sources (such as lighters, mobile phones) into the operation area. Welding, cutting and other open flame operations are strictly prohibited around the storage tanks. If open flame operations are necessary, strict fire approval procedures must be followed, and all flammable and explosive materials around must be cleared, along with adequate fire-fighting equipment being provided.
3.Leak Prevention Measures: In case of a leak of cryogenic liquids, immediately evacuate the surrounding personnel, set up a warning zone, and cut off the source of the leak (if possible); for leaks of flammable media such as LNG, prevent the formation of explosive mixtures; if necessary, activate the emergency response plan and use dry powder fire extinguishers or specialized fire suppressants for handling; for liquid oxygen leaks, stay away from flammable substances such as oils and organic compounds to avoid causing combustion.
4.Emergency Response: Develop a comprehensive emergency plan and equip with emergency rescue supplies (such as first aid kits, leak sealing tools, fire-fighting equipment, etc.); Regularly conduct emergency drills to ensure that operators are proficient in handling leaks, fire suppression, and personnel rescue procedures; In case of severe leakage, explosion, or fire, immediately activate the emergency shut-off valve, evacuate the site, and call the emergency hotline for assistance;
5.Regular Maintenance: According to the equipment maintenance manual, conduct a comprehensive inspection of the storage tanks on a regular basis, including vacuum tests of the insulation layer, calibration of safety valves, inspection of pipeline corrosion, ultrasonic testing of welds, etc. Replace aging or damaged components in a timely manner. It is strictly prohibited to use equipment with potential safety hazards beyond its service life.
Summary
cryogenic storage tanks, as core storage and transportation equipment in key fields such as energy, chemical engineering, and healthcare, their safe and efficient operation directly affects the continuity of production and the safety of personnel and property. Whether it is the technological upgrade brought about by industry development or the core design principle of “thermal insulation to prevent cold loss”, fundamentally, they are all aimed at reducing the gasification loss of low-temperature liquids and avoiding safety risks. In practical applications, operators must strictly follow the requirements of the entire process including pre-job training, standard operation, and regular maintenance. They need to focus on key links such as filling volume, pressure monitoring, cold protection, explosion prevention, and leakage prevention, and also implement emergency plans and emergency drills to fully utilize the storage and transportation advantages of cryogenic storage tanks. With the continuous expansion of the application of low-temperature liquids, adhering to the standardized usage methods and strictly following safety guidelines is not only the foundation for ensuring the service life of the equipment but also the core prerequisite for promoting the healthy and sustainable development of the industry.