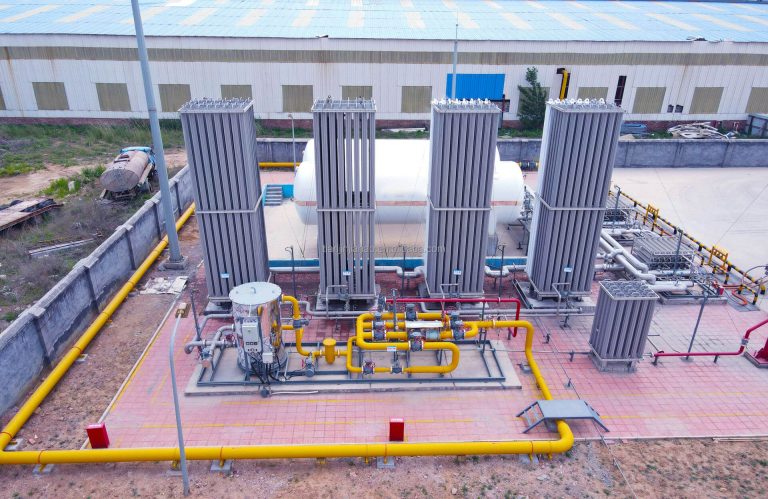
During the operation of liquid nitrogen storage tanks, users often report a problem: the liquid loss exceeds the normal range, which is commonly referred to in the industry as excessive liquid cooling loss. The increase in liquid loss not only affects the economic benefits of equipment operation, but in severe cases, it may even impact the normal production of users.
Why does this situation occur? The following is a detailed explanation of the reasons for the increase in liquid loss.
The influence of welds on the outer shell and outer shell pipeline of liquid nitrogen storage tanks: The welding quality at the connection between the storage tank pipeline and the outer shell or at the outer shell weld does not meet the standards. For instance, in some regions in the south where the weather is humid and acid rain is severe, the outer shell is extremely prone to rust and perforation, allowing outside moist air to enter the interlayer, resulting in a decrease in vacuum degree, an increase in thermal conductivity, and an increase in heat transferred per unit area, causing the daily evaporation rate of liquid nitrogen to exceed the standard.
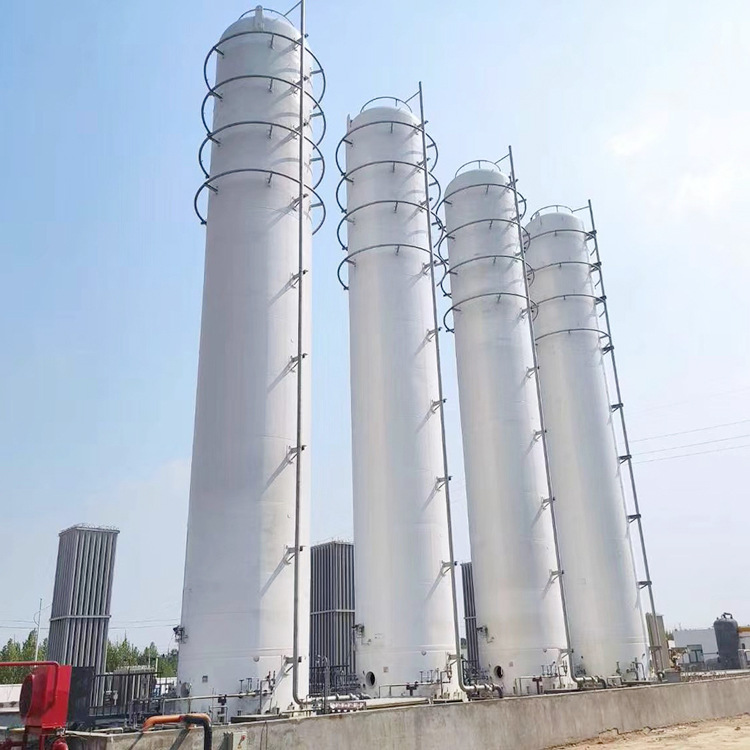

The influence of perlite filling rate: If the perlite between the interlayers is not filled firmly during filling, it will gradually sink during use, leaving no thermal insulation filler in the upper interlayer of the liquid nitrogen storage tank, reducing the cold insulation effect, accelerating heat transfer, and increasing the daily evaporation rate.
The influence of self-pressurization of liquid nitrogen storage tanks: If the valve of the booster does not close tightly or leaks internally, the leaked liquid will vaporize through the booster, causing the pressure of the equipment to continuously rise. When it exceeds the set pressure of the storage tank, it will start to be vented through the automatic vent valve. To maintain its own pressure stability, the liquid will constantly pass through the booster and vaporize before being vented, which will inevitably increase the loss of the liquid in the storage tank. In addition, frost will form on the valve body, and the temperature of the valve body will be lower than that of other parts.
The influence of welds on the inner tank and pipelines of liquid nitrogen storage tanks: Poor welding quality of the inner cylinder and piping causes cracks, resulting in liquid leakage and increased liquid loss. At this point, frost and ice will form at the lower part of the crack, and even the outer cylinder may crack due to freezing.
The above are several main reasons for the increase in liquid loss in cryogenic storage tanks, which are caused by both the manufacturing process and the usage process. Therefore, only by understanding these causes can the increase in liquid loss be avoided and reduced during both the manufacturing and usage processes.