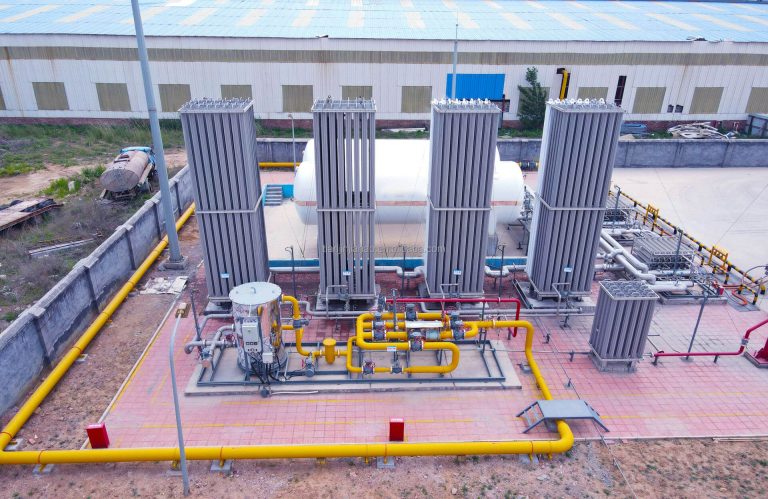
As a low-temperature storage device, liquid argon storage tanks must undergo a meticulous inspection before being filled with liquid argon to ensure the integrity and safety of the equipment. The following are detailed inspection and filling points to help you optimize the operation process and extend the service life of the equipment.
I. Comprehensive Inspection: Prevent potential risks
Before filling liquid argon, the primary task is to thoroughly inspect the outer shell of the storage tank. The integrity of the casing is of vital importance. Any depression or deformation may affect the performance of the equipment. Pay special attention to inspecting the vacuum exhaust port to ensure it is intact. If the exhaust port is damaged, the vacuum degree will be significantly reduced, leading to the failure of insulation. In this case, frost may form on the upper part of the tank, causing a sharp increase in liquid argon loss and even rendering the equipment unusable for a long time. Therefore, conducting an appearance and functional inspection before each use is the key to preventing accidents.
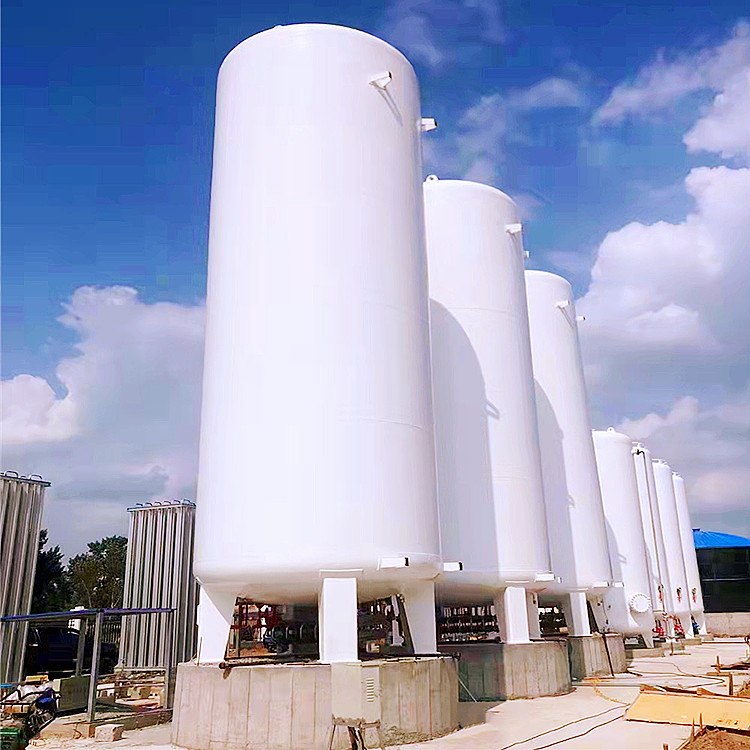

Ii. Fill with caution: Ensure equipment safety
Extra care must be taken when filling with liquid argon. Improper operation may damage the inner tank. For new tanks or those in a dry state, they must be filled slowly and pre-cooled. Rapid cooling can cause the inner tank to crack due to thermal stress, significantly shortening the equipment’s lifespan. In addition, it is essential to avoid direct contact of liquid argon with the vacuum exhaust port; otherwise, the vacuum degree will be reduced and the insulation effect will be affected. The correct filling method includes using dedicated tools to ensure the uniform distribution of liquid argon and prevent local overcooling.
Iii. Best Practices: Enhancing Efficiency and Safety
- Regular maintenance: Establish an inspection plan, record the results of each inspection, and promptly identify and fix problems.
- Operation training: Ensure that operators are familiar with the process and reduce human errors.
- Environmental control: Operate in a well-ventilated area to avoid the risk of liquid argon leakage.
By following these key points, you can not only ensure the safe operation of the liquid argon storage tank, but also optimize equipment performance, reduce losses and improve overall efficiency. Careful inspection and prudent operation are the core for preventing faults and prolonging the service life of equipment.