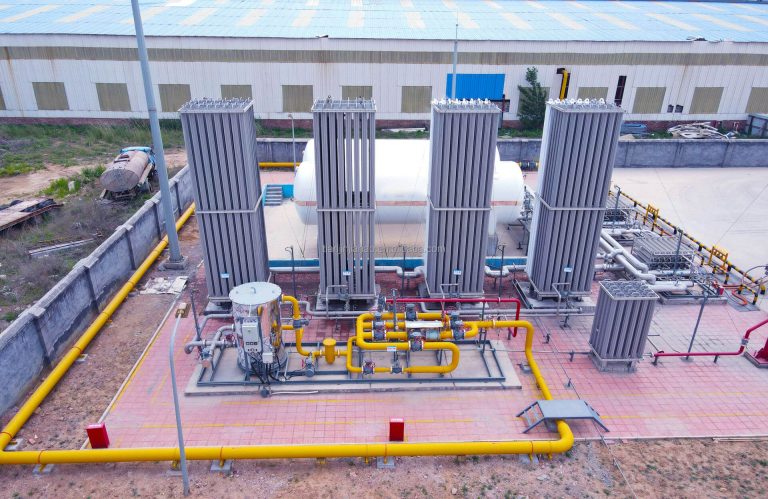
The liquid oxygen storage tank operates in an environment where low temperature and high pressure coexist for a long time. It must rely on reliable safety accessories for real-time monitoring, pressure relief and alarm.
Core Configuration
- Pressure Gauge – Select oxygen-specific type, with a scale limit of 1.5 to 3 times the working pressure, and calibrated every six months;
- Level Gauge – Recommend differential pressure type or radar type, with high and low liquid level audible and visual alarms to prevent overfilling or dry burning;
- Combined Safety Valve – The inner liner must adopt a “safety valve + rupture disk” series structure. The rupture disk before the valve can prevent the valve seat from freezing and sticking, ensuring smooth discharge;
- Pipeline Safety Valve – A small-diameter relief valve must be added between the two stop valves of the liquid phase to prevent the liquid oxygen in the closed section from heating up and vaporizing, causing the pipeline to burst;
- Vacuum and Emergency Cut-off Device – The vacuum degree of the inner layer is ≤ 6.8 Pa. When overpressure occurs, the vacuum valve will automatically open; a pneumatic or liquid phase emergency cut-off valve is set at the root of the storage tank, which can be remotely closed in case of fire.
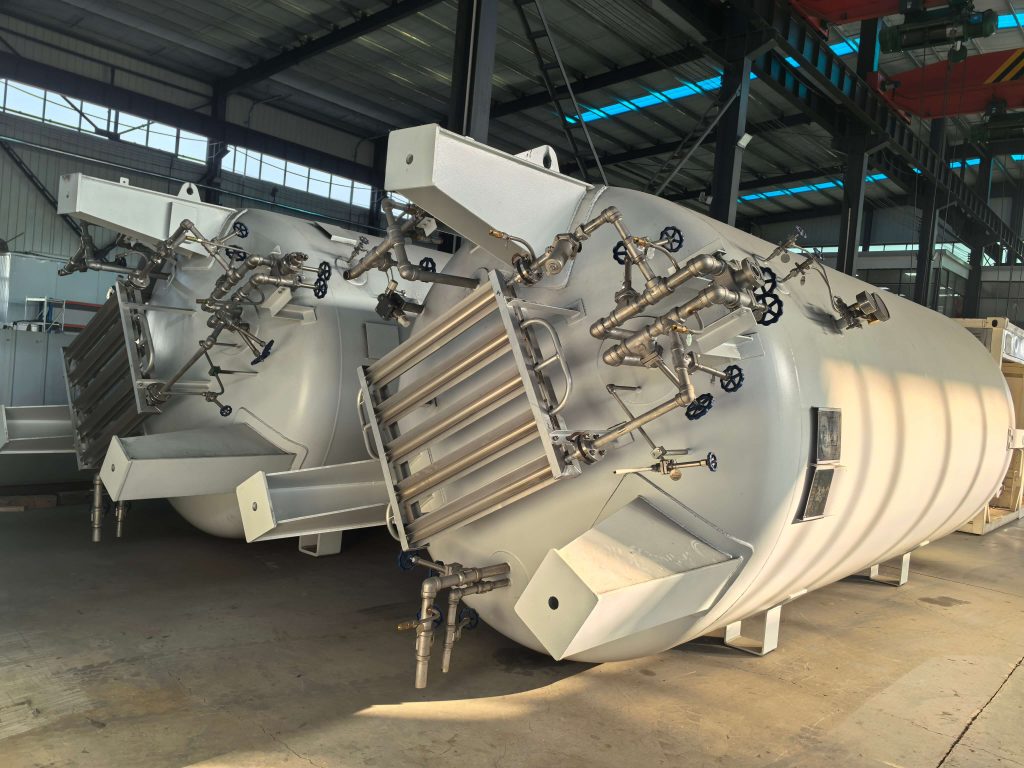

Installation Key Points
The safety accessories and the storage tank body should be designed, manufactured and put into use simultaneously. The valve body material should be selected from austenitic stainless steel or copper alloy to avoid contamination by grease.
The discharge pipe outlet should face an area without people and be equipped with a rain cap and an anti-icing heater to prevent ice and frost from blocking.
Daily Maintenance
Monthly Visual Inspection: No leakage, frosting, or dripping;
Quarterly Hand Testing: Manually lift the safety valve lever to release the air, and confirm the reseating is sensitive;
Half-Yearly Calibration: Send pressure gauges, level gauges, and vacuum gauges to the metrology institution for calibration;
Annual Setting: Re-calibrate the opening pressure of the safety valve on a dedicated test bench. Replace the rupture disc immediately if it has been in use for three years or if there are scratches.
Fault Handling
If abnormal pressure increase in the storage tank, vacuum alarm or leakage of the accessories are detected, the equipment should be immediately shut down, personnel evacuated, and a certified engineer should be contacted for on-site diagnosis. Pressure-tightening is strictly prohibited. Through standardized configuration, regular calibration and rapid response, the operational risks of the cryogenic liquid oxygen storage tank can be significantly reduced, ensuring the safety of personnel and the equipment.