Static electricity poses significant risks in liquid oxygen storage tanks due to the highly flammable nature of oxygen-enriched environments. To mitigate these risks, effective avoidance methods must be implemented during operation, filling, and maintenance processes. This article outlines key strategies to prevent static electricity generation and accumulation, ensuring safe handling of liquid oxygen.
1.Actual Operation of the Water Output from the Liquid Oxygen Storage Tank
The static electricity generated by the flow of liquid oxygen in the pipeline is directly proportional to the square of the water output. Reducing the flow rate is a practical way to minimize static electricity generation during fuel transfer.
2.Prevent Destructive Splashing Electricity Generation
When filling the liquid oxygen storage tank, the static electricity generated by splashing from the top is twice as high as that from the bottom when using subsurface flow. To avoid this, if the bottling method with liquid entering from the top is adopted, the feeding pipe should be inserted to the bottom of the tank to reduce splashing and static electricity production.
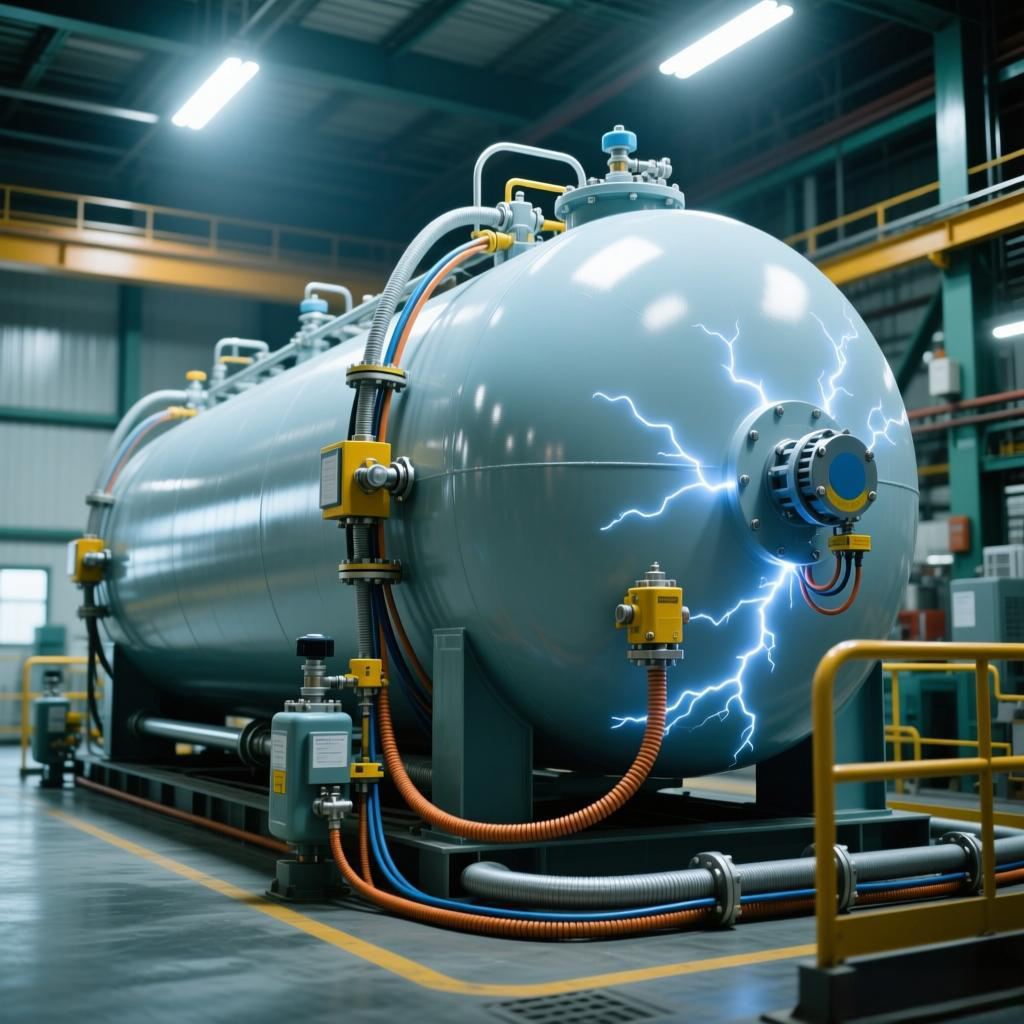

3.Remove Static Electricity from the Body
Workers entering risky areas must wear anti-static shoes, anti-static suits, or cotton knitted work uniforms to prevent static charge buildup on their bodies. Additionally, body static electricity discharge equipment should be installed at the escalator of the liquid oxygen storage tank to safely dissipate any accumulated charges before workers enter the area.
4.Prevent the Accumulation of Static Electricity
The grounding system is the foundation for preventing static electricity and is a critical preventive measure. It consists of two adjacent small metal composite material blocks at the center and flange plates. If the three-way joint is padded with insulating material, a metal composite material jumper wire must be used to ensure continuity. The wire joint resistor of the liquid oxygen storage tank should be maintained regularly to keep the grounding system in optimal condition at all times.
Conclusion
Effective static electricity avoidance in liquid oxygen storage tanks requires a multifaceted approach, including operational adjustments, proper filling techniques, personal protective equipment, and robust grounding systems. By implementing these measures, the risk of static electricity-related incidents can be significantly reduced, ensuring safer operations in oxygen-enriched environments. Regular maintenance and adherence to safety protocols are essential to maintaining a secure working environment.